Rhythm Analysis Method ECG Interpretation
Intro
The five steps of rhythm analysis will be followed when analyzing any rhythm strip. Analyze each step in the following order.
- Rhythm Regularity
- Heart Rate
- P wave morphology
- P R interval or PRi
- QRS complex duration and morphology
Step 1
Rhythm Regularity
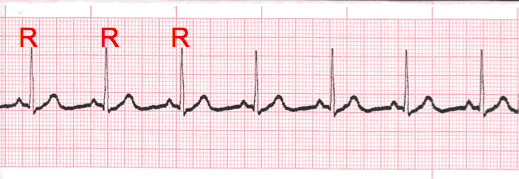
- Carefully measure from the tip of one R wave to the next, from the beginning to the end of the tracing.
- A rhythm is considered “regular or constant” when the distance apart is either the same or varies by 1 ½ small boxes or less from one R wave to the next R wave.
Step 2
Heart Rate Regular (Constant) Rhythms
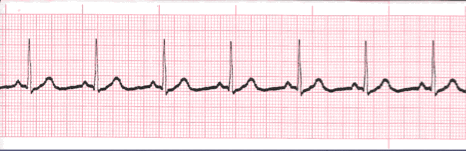
- The heart rate determination technique used will be the 1500 technique.
- Starting at the beginning of the tracing through the end, measure from one R wave to the next R wave (ventricular assessment), then P wave to P wave (atrial assessment), then count the number of small boxes between each and divide that number into 1500. This technique will give you the most accurate heart rate when analyzing regular heart rhythms. You may include ½ of a small box i.e. 1500/37.5 = 40 bpm (don’t forget to round up or down if a portion of a beat is included in the answer).
Step 2 (Cont.)
Heart Rate - Irregular Rhythms
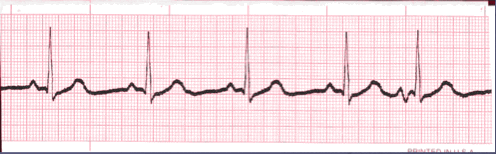
- If the rhythm varies by two small boxes or more, the rhythm is considered “irregular”.
- The heart rate determination technique used for irregular rhythms will be the “six-second technique”.
- Simply count the number of cardiac complexes in six seconds and multiply by ten.
Step 3
P wave Morphology (shape)
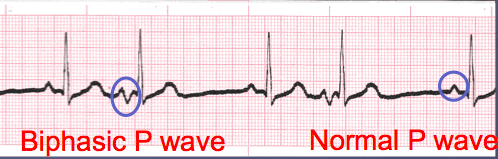
- The lead most commonly referenced in cardiac monitoring is lead II.
- In this training module, lead two will specifically be referenced unless otherwise specified.
- The P wave in lead II in a normal heart is typically rounded and upright in appearance.
- Changes in shape must be reported. This can be an indicator that the locus of stimulation is changing or the pathway taken is changing.
- P waves may come in a variety of morphologies i.e. rounded and upright, peaked, flattened, notched, biphasic(pictured), inverted and even buried or absent!
- Remember to describe the shape. This can be very important to the physician when diagnosing the patient.
Step 4
PR interval (PRi)
- Measurement of the PR interval reflects the amount of time from the beginning of atrial depolarization to the beginning of ventricular depolarization.
- Plainly stated, this measurement is from the beginning of the P wave to the beginning of the QRS complex.
- The normal range for PR interval is: 0.12 – 0.20 seconds (3 to 5 small boxes)
- It is important that you measure each PR interval on the rhythm strip.
- Some tracings do not have the same PRi measurement from one cardiac complex to the next. Sometimes there is a prolonging pattern, sometimes not.
- If the PR intervals are variable, report them as variable, but note if a pattern is present or not.
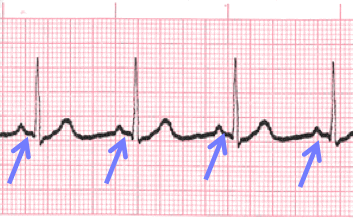
Constant PR Interval
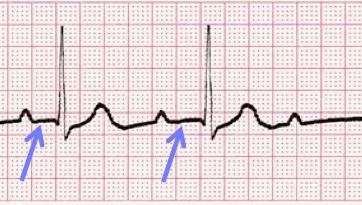
Variable PR Interval
Step 5
QRS complex
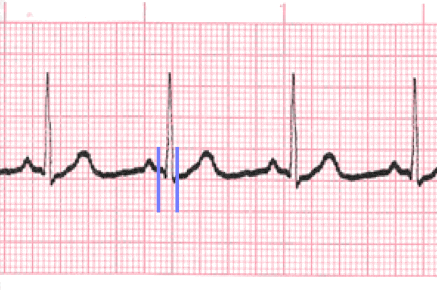
- QRS represents ventricular depolarization.
- It is very important to analyze each QRS complex on the tracing and report the duration measurement and describe the shape (including any changes in shape).
- As discussed in step 3, when referring to P waves, remember changes in the shape of the waveform can indicate the locus of stimulation has changed or a different conduction pathway was followed. It is no different when analyzing the QRS complex. The difference is that in step 3, we were looking at atrial activity. Now we are looking at ventricular activity.
- Measure from the beginning to the end of ventricular depolarization.
- The normal duration of the QRS complex is: 0.06 – 0.10 second
Authors and Sources
Authors and Reviewers
- ECG heart rhythm modules: Thomas O'Brien.
- ECG monitor simulation developer: Steve Collmann
-
12 Lead Course: Dr. Michael Mazzini, MD.
- Spanish language ECG: Breena R. Taira, MD, MPH
- Medical review: Dr. Jonathan Keroes, MD
- Medical review: Dr. Pedro Azevedo, MD, Cardiology
- Last Update: 11/8/2021
Sources
-
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals, 6th Edition
Kathryn Booth and Thomas O'Brien
ISBN10: 1265013470, ISBN13: 9781265013479
McGraw Hill, 2023 -
Rapid Interpretation of EKG's, Sixth Edition
Dale Dublin
Cover Publishing Company -
EKG Reference Guide
EKG.Academy -
12 Lead EKG for Nurses: Simple Steps to Interpret Rhythms, Arrhythmias, Blocks, Hypertrophy, Infarcts, & Cardiac Drugs
Aaron Reed
Create Space Independent Publishing -
Heart Sounds and Murmurs: A Practical Guide with Audio CD-ROM 3rd Edition
Elsevier-Health Sciences Division
Barbara A. Erickson, PhD, RN, CCRN -
The Virtual Cardiac Patient: A Multimedia Guide to Heart Sounds, Murmurs, EKG
Jonathan Keroes, David Lieberman
Publisher: Lippincott Williams & Wilkin)
ISBN-10: 0781784425; ISBN-13: 978-0781784429 - Project Semilla, UCLA Emergency Medicine, EKG Training Breena R. Taira, MD, MPH
-
ECG Reference Guide
PracticalClinicalSkills.com