Overview
Get the inside beat on sinus rhythm! This page offers an introduction to this ECG pattern, as well as providing lessons and sinus rhythm strips for practice.
What is a normal sinus rhythm in ECG?
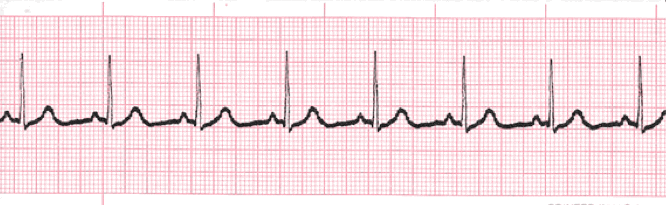
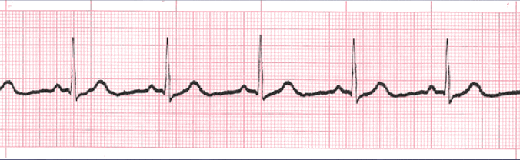
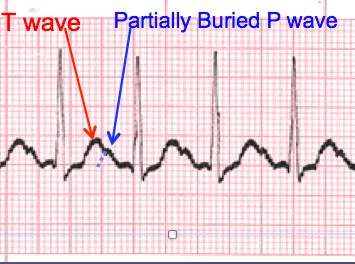
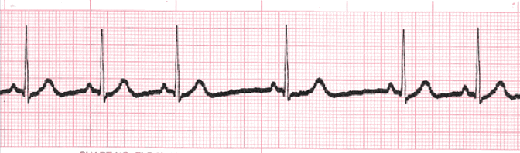
A normal sinus rhythm, seen on an electrocardiogram (ECG) tracing, has a regular heart rate and shape. The cardiac electrical impulse originates in the sinoatrial node (SA), with P waves appearing upright before each QRS complex and having uniform shape. The intervals between the P waves are regular, although some variations can occur with respiration. Sinus rhythms are classified as:
- Normal Sinus Rhythm ECG
- Sinus Bradycardia
- Sinus Tachycardia
- Sinus Arrhythmia
- Sinoatrial Block
- Sinus Pause
Sinus Rhythm Classifications
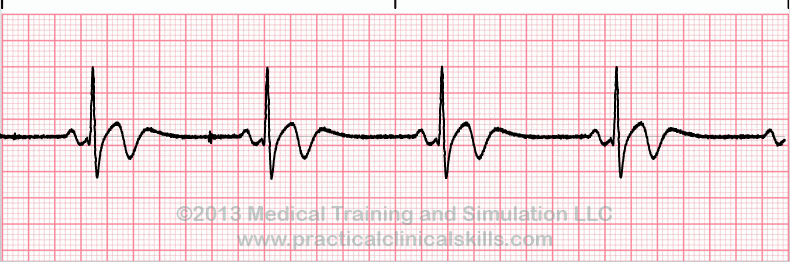
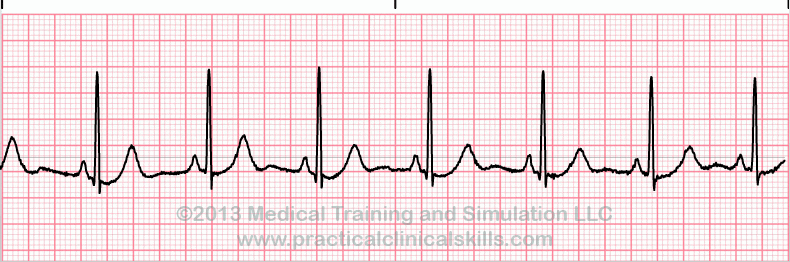
Normal Sinus Rhythm
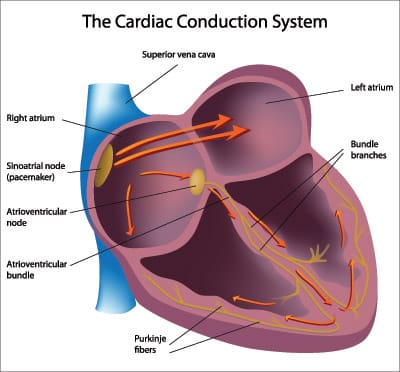
The electrical impulse originates within the SA node and travels through the atria to the AV node. After a brief delay, the impulse travels down the bundle branches via the Purkinje fibers to the ventricles.
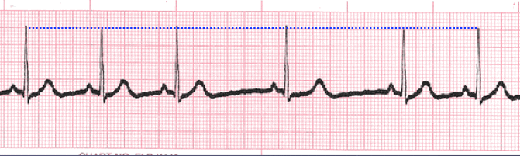
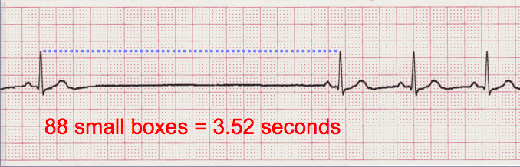
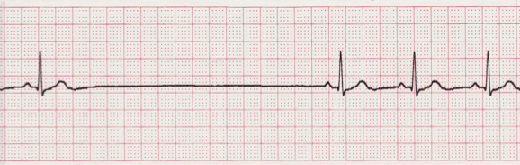
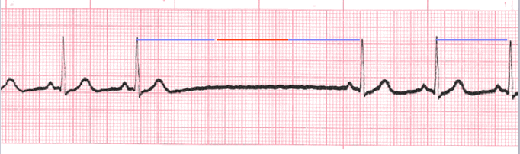
Sinus Pause
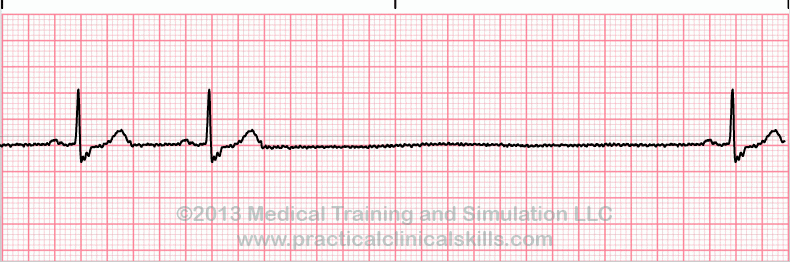
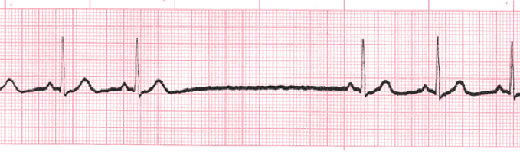
The heart's normal rhythm is driven by signals from the sinoatrial (SA) node, but when sinus arrest occurs this regularity can be thrown off. This happens either with a failure to generate an impulse from the SA node or if there is blockage of transmission. Depending on which type of pause in R-R intervals - known as R-R regularity continues with the beats that follow the missed beat. Depressed ST segments may also be observed. Sinus pause includes sinus arrest and sinus exit block.
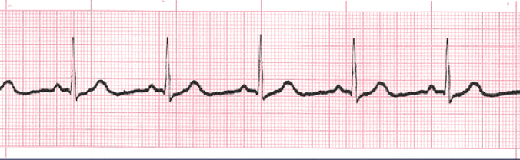
Sinus Arrhythmia
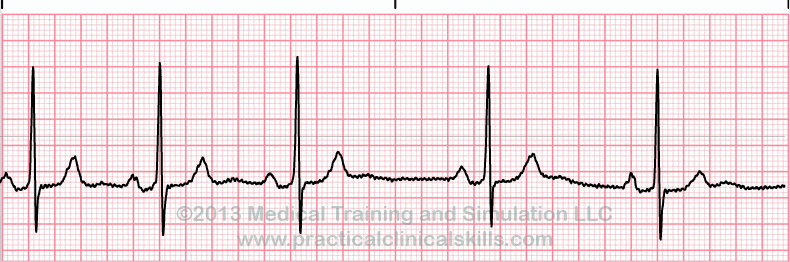
Sinus arrhythmia ECG looks normal with slight irregularities. A common cause of sinus arrhythmia is rhythm variations caused by respiration.
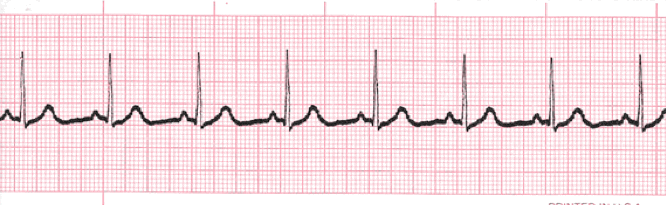
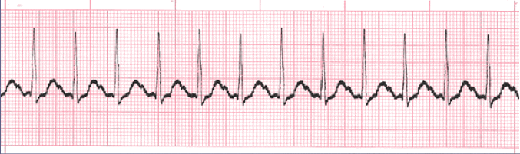
Sinus Tachycardia
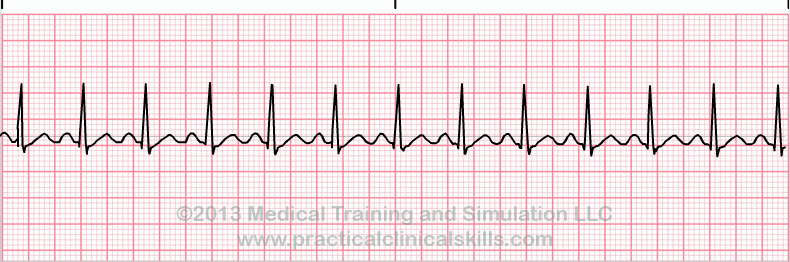
Sinus tachycardia is a normal sinus rhythm with a heart rate over 100 bpm. This occurs with exercise, excitement and with some illnesses.