Heart Sounds & Murmurs
Learn normal and abnormal heart sounds and murmurs with our audio, video and text lessons. Practice drills, quizzes and an abnormal heart/lung sound reference guide. We suggest starting with the heart sounds courses and related quizzes. Begin with normal sounds, then first, second and third/fourth heart sounds, then abnormal murmurs.

Courses
Learn cardiac auscultation. These courses cover abnormal sounds including murmurs, third (S3) and fourth (S4) heart sounds and congenital conditions. Learn these sounds by selecting a topic from the table of contents below. Course and quiz certificates are available for enrolled users.
Fundamentals
An excellent starting point. This free course provides an overview of cardiac auscultation followed by 12 lessons.
Lesson List| 1 | Normal Heart Sounds |
| 2 | Splitting Second Heart Sound |
| 3 | Fixed Splitting Second Heart Sound |
| 4 | Third Heart Sound |
| 5 | Fourth Heart Sound |
| 6 | Innocent Murmur |
| 7 | Mid Systolic Click |
| 8 | Mitral Valve Leaflet Prolapse |
| 9 | Aortic Stenosis |
| 10 | Aortic Regurgitation |
| 11 | Mitral Regurgitation |
| 12 | Mitral Stenosis |
Normal Sounds
This free course teaches auscultation of normal sounds including split and unsplit second heart sounds heard at various heart rates and auscultation points.
Lesson List| 1 | First and Second Heart Sounds - Normal and Unsplit |
| 2 | First Heart Sound (Minimally Split) |
| 3 | Second Heart Sound - Physiologically Split #1 |
| 4 | Third Heart Sound - Physiologic |
| 5 | Innocent Murmur |
| 6 | Exercise - Heart Rate 120 |
First Heart Sounds (S1)
After learning normal heart sounds, take this first heart sounds module.
Lesson List| 1 | First Heart Sound - Loud |
| 2 | First Heart Sound (Minimally Split) |
| 3 | First Heart Sound (Markedly Split) |
| 4 | First Heart Sound - Decreased Intensity |
| 5 | Fourth Heart Sound Plus First Heart Sound |
| 6 | First Heart Sound plus Aortic Ejection Click |
Second Heart Sounds (S2)
Learn about second heart sounds splitting, clicks and plops.
Lesson List| 1 | Second Heart Sound - Physiologically Split #2 |
| 2 | Second Heart Sound with Persistent Splitting |
| 3 | Second Heart Sound with Fixed Splitting |
| 4 | Second Heart Sound: Fixed Splitting, Increased Aortic Intensity |
| 5 | Second Heart Sound: Fixed Splitting, Decreased Aortic Intensity |
| 6 | Second Heart Sound and Late Systolic Click |
| 7 | Second Heart Sound and a Tumor Plop |
| 8 | Opening Snap and Second Heart Sound |
Third & Fourth Heart Sounds
Puzzled by heart sound gallops. Take this short course on third and fourth heart sounds (S3 and S4).
Lesson List
| 1 | Third Heart Sound Gallop |
| 2 | Fourth Heart Sound Gallop |
| 3 | Third and Fourth Heart Sound Gallop |
| 4 | Summation Gallop at 120 beats per minute |
Systolic Murmurs
This systolic murmurs module includes seven lessons each with textual description, audio recording, dynamic waveform video, and a cardiac animation. Optionally, a quiz can be taken to measure comprehension and listening skills.
Lesson List| 1 | Innocent Murmur |
| 2 | Aortic Sclerosis (Musical Murmur) |
| 3 | Aortic Stenosis -Mild |
| 4 | Aortic Stenosis - Severe #2 |
| 5 | Mitral Regurgitation |
| 6 | Mitral Valve Prolapse (Click with Late Systolic Murmur) |
| 7 | Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy |
Diastolic Murmurs
Learn about diastolic murmurs, including regurgitation and mitral stenosis. Before you take this course you should have finished the Normal, First and Second Heart sound, and Extra Heart Sound courses.
Lesson List| 1 | Aortic Regurgitation - Mild |
| 2 | Pulmonic Regurgitation - Mild |
| 3 | Mitral Stenosis - Mild |
| 4 | Mitral Stenosis - Moderate |
| 5 | Mitral Stenosis - Severe |
| 6 | Tricuspid Stenosis - Moderate |
Complex Heart Murmurs
Ready for more advanced heart sounds? Explore complex conditions where there are murmurs in both systole and diastole. Before taking this auscultation course you should be familiar with the previous material on systolic murmurs, diastolic murmurs, extra heart sounds, etc.
Lesson List| 1 | Mitral Regurgitation - Severe |
| 2 | Tricuspid Regurgitation - Severe |
| 3 | Mitral Stenosis Severe and Regurgitation Mild - Rheumatic Origin |
| 4 | Aortic Stenosis Moderate and Regurgitation Mild - Rheumatic Origin |
| 5 | Mitral Regurgitation and Aortic Regurgitation |
| 6 | Acute Pericarditis |
Sudden Death
Learn to identify sounds associated with conditions leading to sudden death. Before taking this course you should have completed the courses concerning heart sounds and murmurs and be comfortable with the material.
Lesson List| 1 | Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy |
| 2 | Aortic Stenosis - Severe #2 |
| 3 | Arrhythmogenic RV Dysplasia |
| 4 | Mitral Valve Prolapse (Click with Late Systolic Murmur) |
| 5 | Myocarditis |
| 6 | Commotio Cordis |
| 7 | Ebstein's Anomaly |
Congenital Heart Sounds
Learn how to identify the heart sounds associated with congenital heart conditions. Before taking this course you should have completed the courses concerning heart sounds and murmurs and be comfortable with the material.
Lesson List| 1 | Coarctation of the Aorta |
| 2 | Patent Ductus Arteriosus |
| 3 | Atrial Septal Defect |
| 4 | Ventricular Septal Defect |
| 5 | Tetralogy of Fallot |
| 6 | Ebstein's Anomaly |
Pediatric Heart Sounds
Improve your ability to properly refer pediatric patients to specialists. Before taking this course you should have completed our courses concerning heart sounds and murmurs and be comfortable with the material.
Lesson List| 1 | 4-month-old girl. Failure to thrive. |
| 2 | 6-month-old boy |
| 3 | 4-year-old with fainting episode |
| 4 | 10-year-old with chest pain. |
| 5 | 6-month-old with poor appetite |
| 6 | 12-year-old with respiratory infections |
| 7 | Twelve-year-old girl with periodic dizziness |
| 8 | Eleven-year-old girl seen after bicycle accident |
| 9 | Eight-year-old girl with elevated temperature |
| 10 | Eight-year-old boy with generalized malaise |
| 11 | Fifteen-year-old boy complains of dizziness |
Carotid Bruit
Listen to examples of carotid bruit using six cases. Learn a method to recognize carotid bruit.
Cases List| 1 | 70yo, annual exam |
| 2 | 85yo, short of breath |
| 3 | 60yo, insur exam |
| 4 | 50yo, arm weakness |
| 5 | 60yo, slurred speech |
| 6 | 65yo, fainting spell |
Auscultation Quizzes
We offer multiple types of graded quizzes, ranging from fundamentals to advanced topics. Quiz scores are saved to your personal dashboard.
Auscultation QuizzesCardiac Auscultation Reference Guide
Our auscultation reference guide includes over one hundred heart sounds. Each lesson includes text, heart/lung sounds, chestpiece location, patient position and waveform and cardiac animations.
Auscultation Reference Guide
Heart Murmurs
Definition
Heart murmurs are sounds produced by turbulent blood flow, particularly from the heart's valves. They can be found in infants or develop later in life. Innocent murmurs frequently resolve without treatment. However, other abnormal heart murmurs indicate a cardiac condition.
Heart Murmur Audio
Stethoscopes are used to listen to heart murmurs. A normal heartbeat sounds like "lub-DUB", which are the sounds of your heart valves closing. This "lub-DUB" sound changes, often with additional sounds being heard.
Cardiac Auscultation
On this website, we provide lessons, reference guides and quizzes for cardiac auscultation of murmurs and other heart sounds. This includes gaining an understanding of cardiac rate and rhythm, conditions of the valves and possible anatomical abnormalities such as congenital defects. Links to our lessons, guides and quizzes are found in the 'Quick Links' box to the left.
Types of Heart Sounds
Heart sounds can include multiple sound components.
- S1: The first heart sound, a low-pitched sound caused by the closing of the mitral and tricuspid valve.
- S2: The secound heart sound, caused by closing of the aortic and pulmonary valve.
- S3: An extra heart sound. S3 is a ventricular gallop, a low-pitched sound that can follow S2.
- S4: An extra heart sound. S4 is an atrial gallop, produced by the atria forcefully pushing blood into a stiff ventricle.
- Systole: The period between S1 and S2, when the ventricles contract.
- Diastole: The period between S2 and the beginning of the next heart beat (S1). Ventricles are relaxing.
- Clicks: These are short, higher-pitched sounds.
- Rubs: A creaking, leather-like sound, typically heard during systole.
Timing and Cadence
Systolic murmurs occur between the first heart sound (S1) and the second heart sound (S2). Diastolic murmurs occur between S2 and S1. In addition, timing is used to describe when murmurs occur within systole or diastole. For example, early systolic, midsystolic or late systolic.
Heart Sounds Location
Where To Auscultate Heart Sounds
Heart sounds auscultation is performed over five locations on the anterior chest wall. Use the stethoscope's diaphragm, switching to the bell to hear lower pitched sounds.
Heart Murmur Location
The recommended heart murmur location on the chest wall is indicated by an icon and text within each of our lessons. Using these auscultation positions can help in evaluating the heart sound or murmur's source.
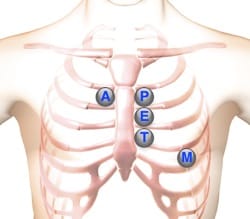
 |
Aortic Valve Area | Second right intercostal space (ICS), right sternal border | |
 |
Pulmonic Valve Area | Second left intercostal space (ICS), left sternal border | |
 |
Erb's Point | Third left ICS, left sternal border | |
 |
Tricuspid Valve Area | Fourth left ICS, left sternal border | |
 |
Mitral Valve Area | Fifth ICS, left mid-clavicular line |
Duration
Heart murmur duration refers to the portion of systole or diastole that the murmur occupies. Terms used include short and long. Murmurs lasting throughout systole are referred to as holosystolic or pansystolic.
Pitch
Evaluation of the murmur's pitch should be made by classifying the pitch (frequency) as low, medium or high. The stethoscope's bell can be helpful with low-pitched sounds while the diaphragm is used for medium or high-pitched sounds.
Shape
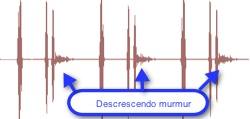
Some murmurs are described by the sound's shape. Common classifications include crescendo (increasing intensity), decrescendo (decreasing intensity), crescendo-decrescendo (increasing then immediate decreasing intensity). Crescendo-decrescendo is also called diamond shaped. Rectangular, also termed plateau indicates a heart murmur of constant intensity. Our lessons include waveforms that illustrate these shapes.

Tonal Quality
Listen for additional aspects of the murmur's sounds. Heart murmurs may have qualities that can be noted as musical, harsh, blowing, booming, sharp or dull.
Respiration and Patient Position
Respiration or patient position can influence murmur intensity as well as heart sound splitting. These factors will be described within the heart sound lessons. Generally speaking, murmurs increasing with expiration originate with left side (aortic or mitral) valves, while murmurs increasing in intensity with inspiration originate with tricuspid or pulmonary valves.
Within each lesson, the author provides a sketch of the patient's position during auscultation, such as supine, left lateral decubitus, squatting or sitting.
Authors and Reviewers
-
Heart sounds by Dr. Jonathan Keroes, MD and David Lieberman, Developer, Virtual Cardiac Patient.
- Lung sounds provided by Diane Wrigley, PA
-
Heart sounds mentorship by W. Proctor Harvey, MD
- Reviewed by Dr. Barbara Erickson, PhD, RN, CCRN.
-
Last Update: 11/10/2022
Sources
-
Heart Sounds and Murmurs Across the Lifespan (with CD)
by Dr Barbara Ann Erickson
Publisher: Mosby
ISBN-10: 0323020453; ISBN-13: 978-0323020459 -
Heart Sounds and Murmurs: A Practical Guide with Audio CD-ROM 3rd Edition
Elsevier-Health Sciences Division
Barbara A. Erickson, PhD, RN, CCRN -
Heart and Lung Sounds Reference Guide
PracticalClinicalSkills.com -
Heart Sounds Made Easy with CD-ROM: (with CD-ROM) 2nd Edition
Anthony P. Salmon
ISBN-13: 978-0443069079 - NCBI Review of Heart Sounds and Murmurs: A Practical Guide
-
The Virtual Cardiac Patient: A Multimedia Guide to Heart Sounds And Murmurs
Jonathan Keroes, David Lieberman
Publisher: Lippincott Williams & Wilkin)
ISBN-10: 0781784425; ISBN-13: 978-0781784429 -
Ventricular Function Curves in the Exercising Dog
JONATHAN KEROES , ROGER R. ECKER , and ELLIOT RAPAPORT
Circulation Research, Vol. 25, No. 5 -
Electrocardiographic changes associated with ritodrine-induced maternal tachycardia and hypokalemia
American Journal of Obstetrics Gynecology, VOLUME 154, ISSUE 4, P921-923, APRIL 01, 1986
Susan K Hendricks, MD, Jonathan Keroes, MD, Michael Katz, MD -
The_Virtual_Cardiac_Patient_A_Multimedia_Guide_to_Heart_Sounds_and_Murmurs
A Multimedia Guide to Heart Sounds and Murmurs
January 2007 JAMA The Journal of the American Medical Association 297(2):217-218
DOI:10.1001/jama.297.2.217. M. Saleem Seyal, MD, Reviewer -
Clinical Heart Disease
W Proctor Harvey, MD
Laennec Publishing; 1st edition (January 1, 2009)
Popular Modules
Normal Heart Sounds
First Heart Sounds
Second Heart Sounds
Third and Fourth Heart Sounds
Systolic Murmur
Diastolic Murmurs
Complex Murmurs
Congenital Abnormalities
Fundamentals of Lung Sounds
Auscultation Quizzes
Free Teaching Resources
Aortic Sclerosis
Aortic Stenosis
Acute Pericarditis
Aortic Regurgitation
Atrial Septal Defect
Cardiomyopathy
Coarctation of the Aorta
Innocent Murmur
Mitral Regurgitation
Mitral Stenosis
Mitral Valve Prolapse
Myocarditis
Pulmonic Regurgitation
Tetralogy of Fallot
Tricuspid Regurgitation Severe
Tricuspid Stenosis
Ventricular Septal Defect
Heart Sounds Audio
Systolic Murmurs
Holosystolic Murmur
First Heart Sounds
Second Heart Sounds
Normal Heart Sounds
S1 Heart Sound
S2 Heart Sound
S3 Heart Sound
S4 Heart Sound
Heart Sounds Associated With Sudden Death
Complex Murmurs
Pediatric Congenital
Diastolic Murmurs
Third Fourth Heart Sounds
?
main Pv# 1 , InitialPages , pix False , #Drops 0 ;
trys 0